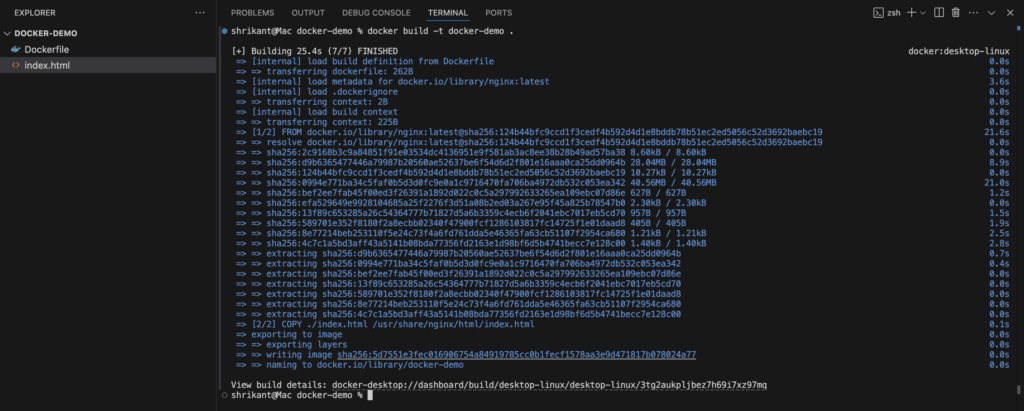
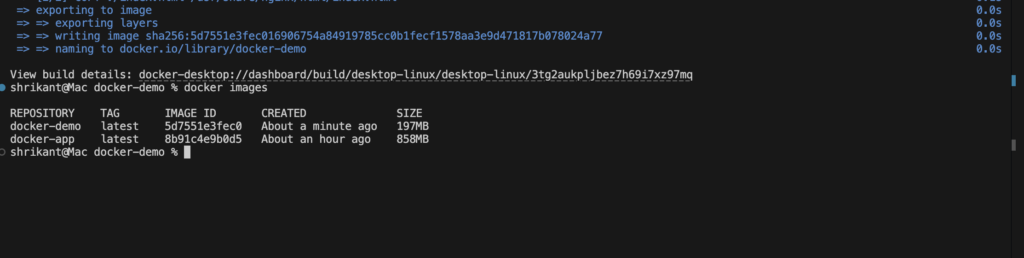
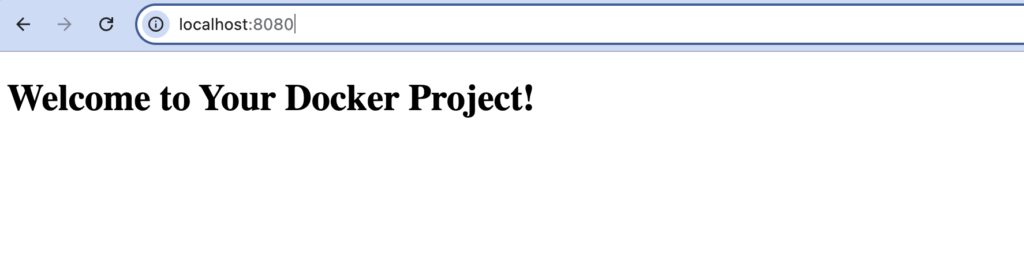
React Native Expo Component List with Examples
React Native Expo provides a rich set of built-in components and APIs to help developers build cross-platform mobile applications efficiently. In this guide, we will explore the React Native Expo component list with examples for UI elements, animations, navigation, and media playback.
1. Basic UI Components React Native Expo Component List
View (Container for UI elements)
import { View, Text } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
return (
<View style={{ flex: 1, justifyContent: 'center', alignItems: 'center' }}>
<Text>Hello, World!</Text>
</View>
);
}
Text (Display text)
import { Text } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
return <Text style={{ fontSize: 20, fontWeight: 'bold' }}>Hello Expo!</Text>;
}
Image (Display an image)
import { Image } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
return (
<Image
source={{ uri: 'https://via.placeholder.com/150' }}
style={{ width: 150, height: 150 }}
/>
);
}
Button (Basic clickable button)
import { Button, Alert } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
return (
<Button title="Click Me" onPress={() => Alert.alert('Button Clicked!')} />
);
}
TextInput (User Input Field)
import { useState } from 'react';
import { TextInput, View, Text } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
const [text, setText] = useState('');
return (
<View style={{ padding: 20 }}>
<TextInput
placeholder="Type here..."
onChangeText={setText}
value={text}
style={{ borderBottomWidth: 1, height: 40 }}
/>
<Text>You typed: {text}</Text>
</View>
);
}
2. List & Scrolling Components React Native Expo Component List
ScrollView (Scrollable container)
import { ScrollView, Text } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
return (
<ScrollView>
{[...Array(20).keys()].map((i) => (
<Text key={i} style={{ padding: 10 }}>Item {i + 1}</Text>
))}
</ScrollView>
);
}
FlatList (Optimized list for large data)
import { FlatList, Text, View } from 'react-native';
const DATA = [{ id: '1', title: 'Item 1' }, { id: '2', title: 'Item 2' }];
export default function App() {
return (
<FlatList
data={DATA}
keyExtractor={(item) => item.id}
renderItem={({ item }) => (
<View style={{ padding: 10 }}>
<Text>{item.title}</Text>
</View>
)}
/>
);
}
3. Expo-Specific Components React Native Expo Component List
import { Camera } from 'expo-camera';
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import { View, Button } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
const [hasPermission, setHasPermission] = useState(null);
useEffect(() => {
(async () => {
const { status } = await Camera.requestCameraPermissionsAsync();
setHasPermission(status === 'granted');
})();
}, []);
return (
<View style={{ flex: 1 }}>
{hasPermission ? <Camera style={{ flex: 1 }} /> : <Button title="Request Permission" />}
</View>
);
}
ImagePicker (Select images from gallery)
import * as ImagePicker from 'expo-image-picker';
import { useState } from 'react';
import { Button, Image, View } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
const [image, setImage] = useState(null);
const pickImage = async () => {
let result = await ImagePicker.launchImageLibraryAsync();
if (!result.canceled) {
setImage(result.assets[0].uri);
}
};
return (
<View>
<Button title="Pick an image" onPress={pickImage} />
{image && <Image source={{ uri: image }} style={{ width: 100, height: 100 }} />}
</View>
);
}
Location (Get user location)
import * as Location from 'expo-location';
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import { View, Text } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
const [location, setLocation] = useState(null);
useEffect(() => {
(async () => {
let { status } = await Location.requestForegroundPermissionsAsync();
if (status === 'granted') {
let loc = await Location.getCurrentPositionAsync({});
setLocation(loc);
}
})();
}, []);
return <Text>Location: {location ? JSON.stringify(location) : 'Fetching...'}</Text>;
}
4. Navigation Components (React Navigation)
Stack Navigation
import { NavigationContainer } from '@react-navigation/native';
import { createStackNavigator } from '@react-navigation/stack';
import { View, Button, Text } from 'react-native';
const Stack = createStackNavigator();
function HomeScreen({ navigation }) {
return (
<View>
<Text>Home Screen</Text>
<Button title="Go to Details" onPress={() => navigation.navigate('Details')} />
</View>
);
}
function DetailsScreen() {
return <Text>Details Screen</Text>;
}
export default function App() {
return (
<NavigationContainer>
<Stack.Navigator>
<Stack.Screen name="Home" component={HomeScreen} />
<Stack.Screen name="Details" component={DetailsScreen} />
</Stack.Navigator>
</NavigationContainer>
);
}
5. Gesture & Animation React Native Expo Component List
TouchableOpacity (Button with Opacity effect)
import { TouchableOpacity, Text } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
return (
<TouchableOpacity onPress={() => alert('Pressed!')} style={{ padding: 10, backgroundColor: 'blue' }}>
<Text style={{ color: 'white' }}>Press Me</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
);
}
Reanimated (Smooth Animations)
import Animated, { useSharedValue, withSpring, useAnimatedStyle } from 'react-native-reanimated';
import { Button, View } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
const offset = useSharedValue(0);
const animatedStyle = useAnimatedStyle(() => ({
transform: [{ translateX: withSpring(offset.value * 100) }],
}));
return (
<View>
<Animated.View style={[{ width: 50, height: 50, backgroundColor: 'red' }, animatedStyle]} />
<Button title="Move" onPress={() => (offset.value = Math.random())} />
</View>
);
}
6. Advanced UI Components
Custom Modal with Animation
import { useState } from 'react';
import { Modal, View, Text, Button, StyleSheet } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
const [visible, setVisible] = useState(false);
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Button title="Show Modal" onPress={() => setVisible(true)} />
<Modal animationType="slide" transparent visible={visible}>
<View style={styles.modalContainer}>
<View style={styles.modalContent}>
<Text>This is a modal</Text>
<Button title="Close" onPress={() => setVisible(false)} />
</View>
</View>
</Modal>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: { flex: 1, justifyContent: 'center', alignItems: 'center' },
modalContainer: { flex: 1, justifyContent: 'center', alignItems: 'center', backgroundColor: 'rgba(0,0,0,0.5)' },
modalContent: { backgroundColor: 'white', padding: 20, borderRadius: 10 },
});
Collapsible Panel (Using react-native-reanimated)
import { useState } from 'react';
import { View, Button, Text } from 'react-native';
import Animated, { useSharedValue, withSpring, useAnimatedStyle } from 'react-native-reanimated';
export default function App() {
const [isOpen, setIsOpen] = useState(false);
const height = useSharedValue(0);
const animatedStyle = useAnimatedStyle(() => ({
height: withSpring(isOpen ? 100 : 0),
}));
return (
<View style={{ padding: 20 }}>
<Button title="Toggle Panel" onPress={() => setIsOpen(!isOpen)} />
<Animated.View style={[{ backgroundColor: 'lightblue', overflow: 'hidden' }, animatedStyle]}>
<Text style={{ padding: 10 }}>This is a collapsible panel!</Text>
</Animated.View>
</View>
);
}
7. Advanced List & Scroll Components
Masonry List (Grid Layout)
import MasonryList from '@react-native-seoul/masonry-list';
import { View, Image, Text } from 'react-native';
const DATA = Array(10).fill().map((_, i) => ({ id: i.toString(), uri: 'https://via.placeholder.com/150' }));
export default function App() {
return (
<MasonryList
data={DATA}
keyExtractor={(item) => item.id}
numColumns={2}
renderItem={({ item }) => (
<View style={{ margin: 5 }}>
<Image source={{ uri: item.uri }} style={{ width: '100%', height: 100 }} />
<Text>Item {item.id}</Text>
</View>
)}
/>
);
}
Parallax Scroll Effect
import { ScrollView, Image, Text } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
return (
<ScrollView contentContainerStyle={{ alignItems: 'center' }}>
<Image source={{ uri: 'https://via.placeholder.com/300' }} style={{ width: '100%', height: 300 }} />
<Text style={{ fontSize: 24, margin: 20 }}>Parallax Effect Example</Text>
</ScrollView>
);
}
8. Advanced Navigation (Deep Linking & Tabs)
Bottom Tabs Navigation
import { createBottomTabNavigator } from '@react-navigation/bottom-tabs';
import { NavigationContainer } from '@react-navigation/native';
import { View, Text } from 'react-native';
const Tab = createBottomTabNavigator();
function HomeScreen() { return <View><Text>Home</Text></View>; }
function ProfileScreen() { return <View><Text>Profile</Text></View>; }
export default function App() {
return (
<NavigationContainer>
<Tab.Navigator>
<Tab.Screen name="Home" component={HomeScreen} />
<Tab.Screen name="Profile" component={ProfileScreen} />
</Tab.Navigator>
</NavigationContainer>
);
}
Deep Linking with Navigation
import { NavigationContainer } from '@react-navigation/native';
import { createStackNavigator } from '@react-navigation/stack';
import { View, Button, Text } from 'react-native';
const Stack = createStackNavigator();
function HomeScreen({ navigation }) {
return (
<View>
<Text>Home</Text>
<Button title="Go to Details" onPress={() => navigation.navigate('Details')} />
</View>
);
}
function DetailsScreen() { return <Text>Details Screen</Text>; }
const linking = { prefixes: ['myapp://'], config: { screens: { Home: 'home', Details: 'details' } } };
export default function App() {
return (
<NavigationContainer linking={linking}>
<Stack.Navigator>
<Stack.Screen name="Home" component={HomeScreen} />
<Stack.Screen name="Details" component={DetailsScreen} />
</Stack.Navigator>
</NavigationContainer>
);
}
9. Advanced Media & Device Features
Video Playback with Expo-AV
import { Video } from 'expo-av';
import { View } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
return (
<View style={{ flex: 1 }}>
<Video
source={{ uri: 'https://www.w3schools.com/html/mov_bbb.mp4' }}
style={{ width: '100%', height: 300 }}
useNativeControls
resizeMode="contain"
/>
</View>
);
}
Audio Recording & Playback
import { Audio } from 'expo-av';
import { useState } from 'react';
import { Button, View } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
const [recording, setRecording] = useState(null);
const [sound, setSound] = useState(null);
async function startRecording() {
const { granted } = await Audio.requestPermissionsAsync();
if (!granted) return;
const { recording } = await Audio.Recording.createAsync(Audio.RECORDING_OPTIONS_PRESET_HIGH_QUALITY);
setRecording(recording);
}
async function stopRecording() {
await recording.stopAndUnloadAsync();
const uri = recording.getURI();
setSound(await Audio.Sound.createAsync({ uri }));
setRecording(null);
}
async function playSound() {
if (sound) await sound.sound.replayAsync();
}
return (
<View>
<Button title={recording ? "Stop Recording" : "Start Recording"} onPress={recording ? stopRecording : startRecording} />
<Button title="Play Recording" onPress={playSound} disabled={!sound} />
</View>
);
}
10. Advanced Animations with Reanimated
Fade-in Animation
import Animated, { useSharedValue, useAnimatedStyle, withTiming } from 'react-native-reanimated';
import { Button, View } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
const opacity = useSharedValue(0);
const animatedStyle = useAnimatedStyle(() => ({ opacity: opacity.value }));
return (
<View>
<Animated.View style={[{ width: 100, height: 100, backgroundColor: 'blue' }, animatedStyle]} />
<Button title="Fade In" onPress={() => (opacity.value = withTiming(1, { duration: 1000 }))} />
</View>
);
}
Additional Resources
For those interested in expanding their skills with APIs, check out our Top 10 Free APIs for Practice in 2025 and improve your JavaScript mastery with our Master ES6 JavaScript – Complete Guide at Master ES6 JavaScript – Complete Guide.